 copyright notice
copyright notice
 accesses since January 4, 2007
accesses since January 4, 2007
Better-than-Nothing Security Practices™
for Securing Web Browsers
v 0.1
Hal Berghel
Jacob Uecker
Paul Braeckel
This web page is a checklist for securing the three most popular web browsers: Microsoft Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox, and
Opera Web Browser. The general perspective taken within this document is to achieve a secure computing environment. The easiest
way to achieve this level of security is to process the list for your particular browser, following the instructions for each item,
and checking off each item along the way. Keep in mind that the points made in this checklist are only recommendations to help
harden the web browser, they are not set in stone. You may find that a certain setting is too strict, in which case you may relax
is particular setting. Keep in mind that this relaxing will impact the level security for your web browsing environment.
Each of these web browsers hold a different portion of the people who surf the World Wide Web. This amount of usage will
typically dictate the amount of attention that creators of malware (a.k.a hackers) will give to the web browser. The general
thought concept behind this checklist is for a web browser user to add an addition layer of defense between themselves and the
World Wide Web. Please keep in mind that each browser is continually being updated to address security issues and provide its
users with new functionality. This will result in new settings and typically the manner in which the settings are presented
to the user. The checklist below were created with the newest versions of each browser and this version number is mentioned for
your reference.
We take no responsibility whatsoever for the implications that these settings will have on your computer. It is suggested to try
these setting changes on a test machine prior to changing your computing infrastructure. We have tried to provide the
consequences of each setting, but there is no doubt many more exist.
Suggests and a comments are always welcomed.
The main intentions behind these settings are to protect the browser user from unknowingly providing personal information to
a potential attacker, and to increase the user's awareness of their browsing environment. While browsing, the user is then able to
make more intelligent decisions without the browser doing something they are unaware of in the background. It is common place for
the browser developers to create options that facilitate the user's browsing experience, however these conveniences often take away
from the security that should be considered while online. The checklist steps that below are followed by a detailed description of
why the steps are necessary.
Copyright © 2003 by Hal Berghel, Jacob Uecker, Paul Braeckel. All Rights Reserved.
 Microsoft Internet Explorer
Microsoft Internet Explorer
Internet Explorer, also known as IE or MSIE, is the proprietary web browser packaged with all versions of Microsoft Windows.
The browser is tightly incorporated in the operating system, and thus adjusting its security settings will result in
securing other products that use the browser's engine (Microsoft Outlook, Microsoft Outlook Express, Microsoft Windows
Updates...). As of October 2005, the most recent official release of Internet Explorer was version
6.0.2900.2180.xpsp_sp2_gdr and was used by 68.9% of the world's web surfers. The following suggestions for the Internet
Explorer web browser will result in a more secure online experience. The end result restricts the functionality of
the browser, however the side effect is a browser that is less prone to malicious software and online attacks. The
settings to be adjusted are located in a tabbed formatted interfaced called Internet Options. To get to
this options window, perform the following four steps:
- Open the Internet Explorer web browser.
- On the Toolbar menu, click Tools pull-down menu.
- Note: The Toolbar menu is the bar at the top of the Internet Explorer window.
- Under Tools, click on the Internet Options... menu option
- This will provide the Internet Options window, which has a tabbed interface for adjusted the
browser's settings.
Internet Explorer divides its Internet Settings into seven (7) tabs. We will be looking at the General, Security, Privacy,
Content, and Advanced tabs. In the instructions that follow, all references are made to the options within the tabbed
window unless specified.
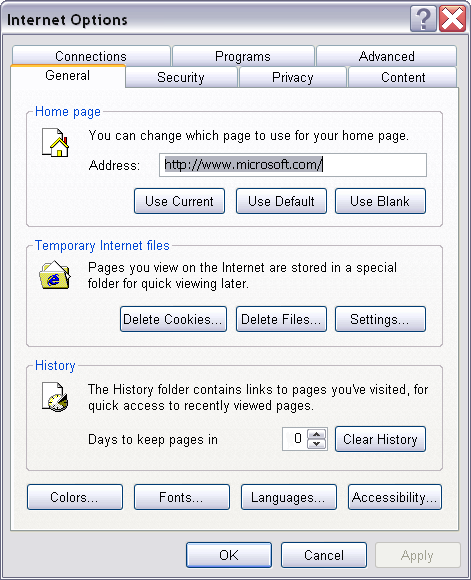 |
- General Internet Options
- Temporary Internet Files
- Click on the General tab.
- In the Temporary Internet files box, click the button Delete Files....
- Click the Settings... button.
- In the Settings window:
- Change the radio button for Check for newer versions of stored pages:
to Every visit to the page .
- Click the OK button.
- Click the OK button.
- Browser History
- Click on the General tab.
- In the History box, click the button Clear History.
- Change the value to the right of Days to keep pages in to zero (0).
- Click the OK button.
- Cookie History
- Click on the General tab.
- Click the Delete Cookies... button.
- In the Delete Cookies window, click the OK button.
- Click the OK button.
- Security Internet Options
- Browser Zones
- Click on the Security tab.
- There are four (4) zones listed under Select a web content zone to specify its security settings.,
click on the first zone Internet.
- In the Security level for this zone box, click on the Default Level button.
- Repeat these two previous steps for zones Local intranet, Trusted sites, Restricted
sites .
- Click the OK button.
- JavaScript
- Click on the Security tab.
- Click on the Internet zone.
- In the Security level for this zone box, click on the Custom Level... button.
- In the Security Settings window:
- Change the setting Java VM - Java permissions to Disable Java.
- Change the setting Scripting - Active Scripting to Disable.
- Click the OK button.
- Click the OK button.
- Privacy Internet Options
- Cookie Handling
- Click on the Privacy tab.
- Click the Advanced... button.
- In the Advanced Privacy Settings window:
- In the Cookies box, check the checkbox in front of Override automatic
cookie handling.
- For the option First-party Cookies, select the radio button Prompt.
- For the option Third-party Cookies, select the radio button Prompt.
- Uncheck the check box in front of Always accept session cookies.
- Click the OK button.
- Click the OK button.
- Pop-Ups
- Click on the Privacy tab.
- Check the checkbox in front of Block pop-ups.
- Click the Settings... button.
- In the Pop-up Blocker Settings window:
- Set the Filter Level: to High: Block all pop-ups.
- Click the Close button.
- Click on the Security tab.
- Click on the Internet zone.
- In the Security level for this zone box, click on the Custom Level... button.
- In the Security Settings window:
- Change the setting Miscellaneous - user Pop-up Blocker to Enable.
- Click the OK button.
- Click the OK button.
- Content Internet Options
- Saved Address Information
- Click on the Content tab.
- In the Personal information box, click on the AutoComplete... button.
- In the AutoComplete Settings window:
- Uncheck the checkbox Web addresses.
- Click the OK button.
- Click the OK button.
- Saved Form Information
- Click on the Content tab.
- In the Personal information box, click on the AutoComplete... button.
- In the AutoComplete Settings window:
- Uncheck the checkbox Forms.
- Click the Clear Forms button.
- Click the OK button.
- Click the OK button.
- Saved Passwords
- Click on the Content tab.
- In the Personal information box, click on the AutoComplete... button.
- In the AutoComplete Settings window:
- Uncheck the checkbox User names and passwords on forms.
- Click the Clear Passwords button.
- Click the OK button.
- Click the OK button.
- Advanced Internet Options
There is a checkbox in front of each of these options to indicate if the option is enabled or disabled.
A check indicates the option is enabled and no check indicates that the option is disabled.
- Advanced: Browsing Options
- Click on the Advanced tab.
- In the Settings: box, scroll down to the Browsing section.
- Check Automatically check for Internet Explorer updates .
- Uncheck Enable Install On Demand(Internet Explorer) .
- Uncheck Enable Install On Demand (Other) .
- Uncheck Enable offline items to be synchronized on a schedule .
- Check Notify when downloads complete .
- Uncheck Use inline AutoComplete .
- Click the OK button.
- Advanced: Java Option
- Click on the Advanced tab.
- In the Settings: box, scroll down to the Java (Sun) section.
- Uncheck Use JRE 1.5.0_04 for <applet> .
- In the Settings: box, scroll down to the Microsoft VM section.
- Uncheck Java console enabled .
- Click the OK button.
- Advanced: Security Options
- Click on the Advanced tab.
- In the Settings: box, scroll down to the Security section.
- Check Check for publisher's certificate revocation .
- Check Check for server certificate revocation .
- Check Check for signatures on downloaded programs .
- Check Do not save encrypted pages to disk .
- Check Empty Temporary Internet Files folder when browser is closed .
- Uncheck Enable Profile Assistant .
- Uncheck User SSL 2.0 .
- Check User SSL 3.0 .
- Check User TLS 1.0 .
- Click the OK button.
 Mozilla Firefox
Mozilla Firefox
Firefox is an open source freeware product developed by Mozilla and evolved out of the Netscape family of products.
As of October 2005, the most recent official released version of Mozilla's Firefox was 1.0.7 was used by 18.8% of the
web surfers in the world. There are four categories of settings to be adjusted and are found within Firefox in the
Firefox Option window. To get to this options window:
- Open the Firefox web browser.
- On the menu bar, click Tools .
- Under Tools, click on Options... menu option.
- This will provide the Options window, which has a tabbed interface for adjusted the
browser's settings.
The left hand side of the Options Window shows five icons, or five categories of settings. We will be looking at
Privacy, Web Features, Downloads, and Advanced. The options for each of these categories are listed in the right
hand window when the icon is highlighted. In instructions that follow, all references are made to the options
within the Options window unless specified.
 |
- Privacy Options
- History
- Click on the Privacy icon.
- If there is a plus sign in front of the History options, expand the History options by clicking on this plus sign.
- Click on the Clear button to the right of History
- Set zero (0) in the textbox Remember visited pags for the last ___ days
- Click the OK button.
- Saved Form Information
- Click on the Privacy icon.
- If there is a plus sign in front of the Saved Form Information options, expand the Saved Form Information options by clicking on this plus sign.
- Click on the Clear button to the right of Saved Form Information
- Uncheck the checkbox in front of Save information I enter in the web page forms and the Search Bar
- Click the OK button.
- Saved Passwords
- Click on the Privacy icon.
- If there is a plus sign in front of the Saved Passwords options, expand the Saved Passwords options by clicking on this plus sign.
- Click the Clear button to the right of Saved Passwords
- Uncheck the checkbox in front of Remembered Passwords.
- Click the OK button.
- Download Manager History
- Click on the Privacy icon.
- If there is a plus sign in front of the Download Manager History options, expand the Download Manager History options by clicking on this plus sign.
- Click the Clear button to the right of Download Manager History.
- In the dropdown box after Remove files form the Download Manager, select When Firefox exists.
- Click the OK button.
- Cookies
- Click on the Privacy icon.
- If there is a plus sign in front of the Cookies options, expand the Cookies options by clicking on this plus sign.
- Click the Clear button to the right of Cookies.
- Uncheck the checkbox in front of Allow sites to set cookies.
- Click the OK button.
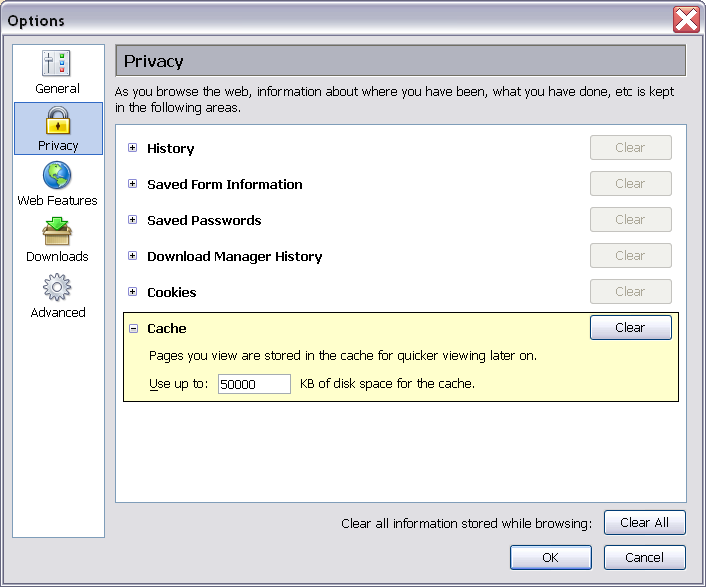
- Cache
- Click on the Privacy icon.
- If there is a plus sign in front of the Cache options, expand the Cache options by clicking on this plus sign.
- Click the Clear button to the right of Cache.
- Click the OK button.
- Web Features
- Block Popup Windows
- Click on the Web Features icon.
- Check the checkbox in front of Block Popup Windows.
- Click on the button Allowed Sites.
- In the Allowed Sites window that opens, click Remove All Sites.
- In the same window, click the OK button.
- Click the OK button.
- Allow web sites to install software
- Click on the Web Features icon.
- Uncheck the checkbox in front of Allow web sites to install software.
- Click on the button Allowed Sites.
- In the Allowed Sites window that opens, click Remove All Sites.
- Click the OK button.
- Load Images
- Click on the Web Features icon.
- Check the checkbox in front of Load Images.
- Check the checkbox in front of for the originating web site only.
- Click the OK button.
- Enable Java
- Click on the Web Features icon.
- Uncheck the checkbox in front of Enable Java.
- Click the OK button.
- Enable JavaScript
- Click on the Web Features icon.
- Uncheck the checkbox in front of Enable JavaScript.
- Click the OK button.
- Downloads
- Download Folder
- Click on the Downloads icon.
- In the Download Folder box, select the radio button in front of Save all files to this folder:.
- In the dropdown box after Save all files to this folder:, select Other...
- In the Browser for folder window:
- Scroll to the top of list of folders and highlight the Desktop folder by clicking on it.
- Click on the Make New Folder button.
- Type the name "Downloads" for this folder. This is the folder on your Desktop where all your downloads will now be saved.
- Click the OK button.
- Click the OK button.
- Download Manager
- Click on the Downloads icon.
- In the Download Manager box:
- Check the checkbox in front of Show Download Manager window when a download begins.
- Uncheck the checkbox in front of Close the Download Manager when all downloads are complete.
- Click the OK button.
- File Types
- Click on the Downloads icon.
- In the File Types box, highlight the first item in the box under Automatically perform the associated action with each of the following file types: by clicking on it.
- Click on the Remove button.
- Repeat this process to remove all entries listed in this box.
- Click the OK button.
- Advanced Options
- Software Update
- Click on the Advanced icon.
- Scroll down to the Software Update option in the right hand pane.
- If there is a plus sign in front of the Software Update option, expand the Software Update option by clicking on this plus sign.
- Check the checkbox in front of Firefox.
- Check the checkbox in front of My Extensions and Themes.
- Click on the button Check Now.
- When Firefox is finished looking for updates and installing them, click the Finish button.
- Click the OK button.
- Security
- Click on the Advanced icon.
- Scroll down to the Security option in the right hand pane.
- If there is a plus sign in front of the Security option, expand the Security option by clicking on this plus sign.
- Uncheck the checkbox in front of Use SSL 2.0.
- Check the checkbox in front of Use SSL 3.0.
- Click the checkbox in front of User TLS 1.0
- Click the OK button.
- Certificates
- Click on the Advanced icon.
- Scroll down to the Certificates option in the right hand pane.
- If there is a plus sign in front of the Certificates option, expand the Certificate options by clicking on this plus sign.
- In the Client Certificate Selection box, check the radio button Ask Every Time.
- Validation
- Click on the Advanced icon.
- Scroll down to the Validation option in the right hand pane.
- If there is a plus sign in front of the Validation option, expand the Validation option by clicking on this plus sign.
- In the OCSP box, select the radio button in front of Use OCSP to validate only certificates that specify an OCSP service URL.
 Opera Web Browser
Opera Web Browser
Opera is a freeware browser developed by Opera Software is Oslo, Norway. As of October 2005, the most official released version
of Opera Software's Opera browser was 8.5 and 1.1% of the web servers in the world. The settings to be adjusted are found
in the Opera Preferences window. To get to this options window:
- Open the Opera web browser.
- On the menu bar, click Tools pull-down menu.
- Note: The Toolbar menu is the bar at the top of the Opera window.
- Under Tools, click on the Preferences... menu option.
- This will provide the Preferences window, which has a tabbed interface for adjusted the
browser's settings.
Opera divides its Preferences into four (4) tabs: General, Wand, Web pages, Advanced. We will look at the settings under
the General, Wand, and Advanced tabs. In instructions that follow, all references are made to the options within the
Preferences window unless specified.
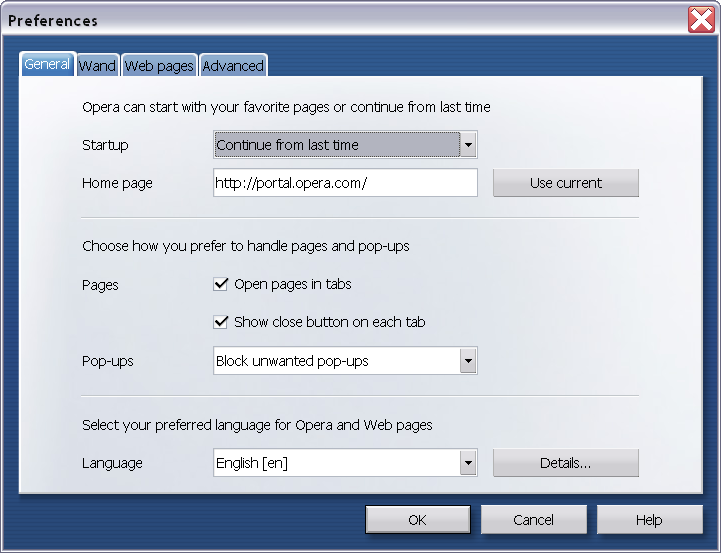 |
- General Preferences
- Pop-ups
- Click on the General tab.
- In the drop down list to the right of Pop-ups, select Block unwanted pop-ups .
- Click the OK button.
- Wand Preferences
- The Wand
- Click on the Wand tab.
- Uncheck the checkbox in front of Let the Want remember passwords .
- Click the Passwords button.
- In the Server manager window:
- Uncheck the checkbox in front of Cookies .
- Check the checkbox in front of Wand logins .
- Remove each entry by clicking on it followed by clicking the Delete button.
- Click the Close button.
- Click the OK button.
- Personal Information
- Click on the Wand tab.
- In the fields under Opera can auto-complete forms with your personal information, delete any
personal information in these fields.
- Click the OK button.
- Advanced Preferences
- Java Options
- Click on the Advanced tab.
- In the list of advanced options on the land hand pane, click on the Content group of options.
- Uncheck the checkbox in front of Enable JavaScript .
- Uncheck the checkbox in front of Enable Java .
- Click the OK button.
- Downloads Options
- Click on the Advanced tab.
- In the list of advanced options on the land hand pane, click on the Downloads group of options.
- Under Download directory, click on the Choose button.
- In the Browse For Folder window:
- Browse to the Desktop, which is typically the directory at the top of the directory tree.
- Highlight this Desktop directory by clicking on it.
- Click the Make New Folder button.
- Type the name "Downloads" for this folder. This is the folder on your Desktop where all your downloads will now be saved.
- Click the OK button.
- Click the OK button.
- Browser History and Cache Options
- Click on the Advanced tab.
- In the list of advanced options on the land hand pane, click History group of options.
- Change the drop-down menu for Typed in addresses to zero (0).
- Click on the Clear button to the right of Typed in addresses.
- Change the drop-down menu for Visited Addresses to zero (0).
- Click on the Clear button to the right of Visited Addresses.
- Change the drop-down menu for Memory cache to Off .
- Change the drop-down menu for Disk cache to Off .
- Click on the Empty now button to the right of Disk cache.
- Check the checkbox in front of Empty on exit .
- Click the OK button.
- Cookie Options
- Click on the Advanced tab.
- In the list of advanced options on the land hand pane, click Cookies group of options.
- Change the drop-down menu for Normal cookies to the Let me decide every time I receive one option.
- Change the drop-down menu for Third party cookies to the Let me decide every time I receive one option.
- Click on the Manage cookies... button.
- In the Server manager window:
- Check the checkbox in front of Cookies .
- Uncheck the checkbox in front of Wand logins .
- Remove each entry by clicking on it followed by clicking the Delete button.
- Click the Close button.
- Check the checkbox in front of the Delete new cookies when exiting Opera option.
- Uncheck the checkbox in front of the Accept cookies with incorrect paths option.
- Check the checkbox in front of the Use cookies to trace password protected pages option.
- Click the OK button.
- Security Options
- Click on the Advanced tab.
- In the list of advanced options on the land hand pane, click Security group of options.
- Click on the Security protocols... button.
- In the Security protocols window:
- Uncheck the checkbox in front of the Enable SSL 2 option.
- Check the checkbox in front of the Enable SSL 3 option.
- Check the checkbox in front of the Enable TLS 1 option.
- Check the checkbox in front of the Enable TLS 1.1 option.
- In the list under Select ciphers to enable , uncheck all Cipher with Version SSL 2.
- In the list under Select ciphers to enable , uncheck all Cipher less than 128 bit.
- Click the OK button.
- Check the checkbox in front to the Warn me before submitting forms insecurely option.
- Click the OK button.
Detailed Descriptions
Internet Explorer: General Internet Options
- Internet Explorer's General Options provides the user with options to handle information that has been previously
stored by the browser and the space it uses to store this information.
Internet Explorer: Temporary Internet Files
- Why do this?
- When a webpage is accessed, the browser will save the webpage locally on the computer, this is referred to as caching
the webpage. The next time this webpage is accessed, the browser will check if it has been previously cached, and
if it has been cached, it will load the webpage from the locally cached copy. The intention here is to expedite the
user's browsing experience, because the browser does not need to download the webpage again, however, this in effect
leaves a trail of web pages that have been viewed by the browser. In order for the browser to reload the webpage,
this cached information includes all of the necessary elements (HTML, images, scripts...) required to display the
web page, saved as files. Like any other file on saved on the computer, this information may be accessed by
searching the computers file system directories. By setting this value to zero, the cache is effectively disabled,
and there are no temporary internet files cached on the computer. It is suggested that this cache be disabled
to avoid anyone or any software, such as malware and spyware, from accessing the cache of the visited web pages,
and harvesting information about the user.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- The user's browsing experience will be slightly slower due to the browser downloading a webpage every time that
the user wants to view this particular webpage. With faster Internet connections this is not as large a concern
because the browser is able to quickly download the webpage resulting in no need for temporary browser files on the
computer. However, this will be very obvious in a computer environment where the Internet connection is slower,
such as with dial-up connectivity. Aside from this speed concern, it should be noted that when a browser uses the
cached version of a webpage, it is displaying what has been previous downloaded, if updates have been made to this
webpage, the user will not be viewing these updates. Therefore, by disabling the cache, the user will always be
viewing the most recent updates to the web pages that they are accessing.
- Return
Internet Explorer: Browser History
- Why do this?
- This browser will remember links to the websites that it has recently visited. This is convenient for the user
because the browser has a track-record of the web pages they have visited, which may be referenced to recall sites that
were of interest to the user. The concern is that this track-record may also be of interest to the someone or some
software. By setting the value to zero, the browser history is in effect disabled. The result of disabling the
browser’s history is that attackers, malware, and spyware are not able to harvest surfing trend information and other
personal information about the user from the browser's history log.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- This may have inconvenient for the user because they are not able to reference URL addresses in the Browser
History of web pages that they have recently visited. However, the user may also achieve the history effect by
creating Bookmarks for each desired URL address. It is suggested to keep these bookmarks external to the browser
so this information is also not stored within the browser and potentially available to an attacker.
- Return
Internet Explorer: Cookie History
- Why do this?
- Cookies and the manner in which the browser handles them are discussed in more detail in the
Internet Explorer: Cookie Handling section. Clearing the Cookie History will delete any cookies that are currently
saved within the web browser. This is suggested because it will give the user a clean slate with respect to cookies, and
any remnants of personal information that may be stored within these cookies. As with any information stored within
the browser, it is convenient for the user but also potentially accessible by an attacker.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- If the user has previously accepted cookies from a what is viewed as a trusted website, the information that was
saved by the cookie setting website will be lost. There is no set standard for the information that is set
within a cookie, but it is generally viewed as a means to identify the user, actions that they have made, progress
made will viewing the web site, usernames and passwords, the computer being used, and typically result in a
customize appearance of the website for the user after the initial setting of the cookie. This is referred to as
"saving state", which in laymen's terms basically means letting the webpage know what happen the last time the user
interacted with it. If the webpage is not able to determine its state, it will not be able to provide coherent
interaction with the user and the user will not be able to view the intended purpose behind the webpage.
- Return
Internet Explorer: Security Internet Options
- Internet Explorer's Internet Options determine how the browser will react to the content that is delivered by a website.
When the user enters the URL of a website, they request the server that hosts the website to download whatever content that
is associated with that particular web page. This may include Active X components, Java applets, JavaScript, software
downloads, and pop-ups among other possibilities. Security options will dictate how the browser deals with each of these
elements.
Internet Explorer: Browser Zones
- Why do this?
- The Internet Explorer approach towards security is a zone-based, which means that all websites are divided into one
of four zones: Internet, Local intranet, Trusted sites, and Restricted sites. By default, the browser places all the
websites initially into the Internet zone. The user is then able to re-allocate any web site addresses into any of
these four zones, each of which has its own security settings and access privileges. By properly setting the
security levels of each of these zones, Internet Explorer ensures that all websites will conform to and maintain a
good level of security. For ease of use, the browser provides a predefined security settings called a Default
Level of security, which is considered safe functional browsing and appropriate for surfing most web sites. The user
may then adjust the security settings associate with each of the four zones as they see fit. It is suggested to set
each of these zone to this default level of security. Extreme care should be taken when allocating a website to one
of the four zones, because the Default Level of security for each of the zones is different; the Default Level for the
Internet zone is much higher than the Default Level for the Trusted sites. It is suggest to keep all websites in the
Internet zone.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- The default settings are considered to be on the higher end of security spectrum, the user should not experience any
changes in your browsing experience.
However, in order to allow Internet Explorer to update itself via Microsoft's online updates, the user must allocate
several websites as Trusted sites. This will allow the user to keep current on software updates. This may be achieved
as follows:
- On the Internet Explorer Toolbar menu, click on the Tools menu.
- Under the Tools menu, click on the Internet Options... menu option.
- In the Internet Options window, click on the Security tab.
- Click the Trusted sites web content zone.
- Click the Sites... button./
- In the box under Add this Web site to the zone:, type http://*.windowsupdate.microsoft.com
- In the box under Add this Web site to the zone:, type http://*.windowsupdate.com
- Verify that these two site are listed in the box below Web sites:.
- Uncheck the checkbox in front ofRequire server verification for all sites in this zone.
- In the Trusted sites window, click the OK button.
- Click the OK button.
- Return
Internet Explorer: JavaScript
- Why do this?
- JavaScript is a scripting language used to build web pages and integrated directly into the webpage's HTML code. The
intention behind JavaScript is to elevate the work load on the server, allowing the user's computer to do some of the
webpage processing, and to build advanced webpage features into the webpage. The result is that the user's webpage
interaction is much more responsive since the webpage does not need to return to the web server in order to process
webpage information. JavaScript is also able to create custom web page building blocks, such as form elements
(drop down interactive menus, submit buttons...). Although there is an added benefit to the user for using JavaScript,
the scripts are actually code snippets that is technically executed on the user's computer, without the user given the
option to run or not to run the script. It is never a good idea for the user to let a webpage execute code on their
computer without their consent. This is the source of numerous malware attacks. It is for this reason the suggested
setting is to disable JavaScript with Firefox.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- If JavaScript is disabled, Internet Explorer will not allow any of the functionality achieved through the
embedded scripting. This will impact your browsing experience because the content provided by web sites for
legitimate purposes will be blocked. The benefit though is that the potential threat from Java based malware is
eliminated.
- Return
Internet Explorer: Privacy Internet Options
- Internet Explorer's Internet Privacy options determine how the browser will handle cookies and pop-ups that the
website sends to the user, when the user requests a webpage.
Internet Explorer: Cookie Handling
- Why do this?
- A cookie is information that is sent by a webpage to your browser when a webpage is accessed, stored locally
as a file on the user's computer, and used to identify the user or the actions that the user has performed. A copy
of this cookies is then sent back by the browser to the server every time browser access a webpage on that
particular server. Since it is theoretical impossible for a web server to track every user that accesses one of its
web pages on the web server, a cookie is used to store information about the user's interaction with the webpage on
the user's computer. This information stored in the cookie is typically unique to that the user's browsing experience.
For example, a cookie may contain information for an online shopping cart to keep track of and tell the website what
the person has chosen to purchase, or a cookie may contain a identification number that the web server uses to track
the user's activity from visit to visit. Since this sensitive information is used to identify a user, disabling cookies
will not allow the browser to accept cookies and potentially store sensitive personal information that might be accessed
by an attacker. In reference to the examples, if an attacker where access a cookie that contained part numbers that a person
was ordering from a website, the attacker could adjust the order, or if the attacker was able to steal the user's identification
number for a website, they could impersonate that user by placing a copy of the cookie on their machine.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- Since a large portion of web pages use cookies in order to store information about the user's interaction with the web site,
disabling cookies will significantly impact the user's browsing experience. For example, many e-commerce sites and
bulletin boards will be render unusable because they track user progress through cookie data. If it is necessary to
view a webpage that requires cookies, the browser may be told to accept cookies from a website as follows:
- Click the Sites... button.
- In the Per Site Privacy Actions window, below Address of the web site: in the
Per Site Privacy Actions window, enter the URL of the webpage that will be allowed to set
cookies on the computer.
- Click on the Allow button.
- In the list below Managed Web sites:, confirm the entered website and the "Always Allow" setting.
- Click the OK.
This same process may be used to block cookies from a specified web site as well. It is suggested to remove all sites
from this list of Managed Web sites that say "Always Allow" unless the user has decided to allow that particular
website to set cookies. The user must keep in mind here that this will allow the entered web site to set cookies,
so sensitive information may be available for a malware attack and caution should be taken to protect this
information stored in the cookies.
- Return
Internet Explorer: Pop-Ups
- Why do this?
- Pop-ups are windows that are automatically opened by the browser forcing the user to view the displayed information.
Although some websites use pop-ups legitimately to show information that is pertaining to but not part of the website's
information, generally they are used as online advertising and considered annoying. The default setting for Internet
Explorer is for it to block pop-ups, and this is the suggested setting to reduce the annoying nature of a popup.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- Some sites do make legitimately usage of pop-ups. For example, a text website might provide a link that, when clicked,
would open a popup window to display an image that is referred to in the website text. If pop-ups are blocked, then
Firefox would not allow the web site to open the popup and the link would appear to be functionless. You may enter a
website as a trusted website, allowing it to open pop-ups, by performing the following steps:
- Click on the Settings... button to the right of Block Pop-ups.
- In the Pop-up Blocker Settings window that opens:
- Enter the exact URL of the website you want to allow pop-ups into the box under
Address of Web site to allow:.
- Click the Add button.
- Repeat this steps to add additional websites.
- Click the Close button.
You will note that the website that you entered is listed on the Allowed sites: window. The website that you
entered will be now be allowed to use pop-ups. If there are other websites listed in the Allowed
sites: window, you can remove them as follows:
- Click on the Settings... button to the right of Block Pop-ups.
- In the Pop-up Blocker Settings window that opens:
- Click on the Remove button.
- Repeat this steps to remove additional websites.
- Click the Close button.
- Click on the OK button.
- Return
Internet Explorer: Content Internet Options
- Internet Explorer's Internet Content options determine how the browser will authentification certificates and user
information. Certificates are user to verify that communications between the browser and the server that the browser is
communicating with are secure. User information is the information that the browser learns about the user from the
user entering information into the browser and web forms.
Internet Explorer: Saved Address Information
- Why do this?
- As the user types a URL into the Internet Explorer address bar, they will be provided a list of matching URL address
in the form of a list of URLs that match what they have typed. The intention here is to facilitate the user having to
type in URLs that they visit before, they may type the first portion of the URL and then scroll down to the desired
URL address. It is suggested to minimize the amount of information that the browser stores about the user, because
any information that is known by the browse is stored as a file on the computer and may be accessible to prying
eyes. This setting is very similar to the Browser History in the General Internet options, and the two should be used
in conjunction with each other.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- This may have a slightly inconvenient for the user since they are required to enter an entire webpage URL
before every visit to a website. The benefit is the user's surfing trends are not stored by the browser and
potentially accessible to malware attacks.
- Return
Internet Explorer: Saved Form Information
- Why do this?
- The browser will remember information that is entered into webpage forms and the browser Search Bar. The intention
here is to facilitate the user's web browsing experience by automatically making suggestions when you repeated
enter form information. It is best to not allow the browser to save any information that is entered into a web form.
Although it is convenient for the user to have the browser complete webpage forms, it is just as easy for malware to
access this saved information.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- This may have a slightly inconvenient for the user since they must enter webpage form information on every visit
to a website, but otherwise have no effect on the user's browsing experience.
- Return
Internet Explorer: Saved Passwords
- Why do this?
- The browser will remember user passwords that are entered into webpage login forms in its Password Manager. The
intention here is convenience for the user not to recall their username and password when visiting sites that require
them to login in order to access the webpage. For example, with this option is enabled, when the user enters a new
username and password, the browser will prompt the user if they would like to save this information. If the user
selects "Yes", the next time they start to input their username, they will be provided with a list from which they may
select the username and the password will automatically be inserted. This may be very convenient for some users for
example with online banking account; when they access this banking web site from the browser with their password saved,
the browser will provide them enter their password. It is best to disable the browser's ability to recall user
passwords. Although it is convenient for the user let the browser manage login information every time they access
a website that requires login, it is just as easy for malware to access this saved information.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- This may be a slightly inconvenient for the user since they must enter their password on each website that
requires a password, but it will significantly reduce the ability of malware to capture their password information.
There are password managers that are not associated with browsers and more secure at managing password information.
- Return
Internet Explorer: Advanced Internet Options
- Internet Explorer's Internet Advanced options provide the advanced user with the esoteric browser settings that allow
the user to fine-tune their browsing experience to achieve, among other things, a more secure browsing experience. The
areas that will be addressed are grouped under Browsing, Microsoft Virtual Machine, and Security. The settings are
enabled or disabled by checking or unchecking the checkbox in front of the listed option. These settings should be
adjusted only by the more advanced Internet Explorer user.
Internet Explorer: Java Option
- Why do this?
- Java is a popular platform-independent programming language that is able to create web applications, however it is a common
target for malware authors. Malware takes advantage of the fact that it is executable code, which is typically automatically
downloaded and executed on your computer. Numerous exploits exist that use Java to compromise a computer and the data stored
on it. Disable Java within Internet Explorer by unchecking this feature, this is the suggested setting for this option due to
Java's popularity as a language for creating malware.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- Java is self standing application called an applet that is used to create interactive web content (games, animations,
printing features...) and web based applications (mortgage calculators, image manipulations, virus scanners...). If java is
not disabled, Internet Explorer will not allow any of the functionality achieved through the Java applets. This will impact
your browsing experience because the content provided by web sites for legitimate purposes will be blocked. The benefit
though is that the potential threat from Java based malware is eliminated.
- Return
Internet Explorer: Browsing Options
- Why do this?
- When the user enters a legitimate URL in the address bar of the browser, the web server hosting the website for this URL
downloads the contents of the webpage to the user's browser. These Browsing options determine how Internet Explorer
will handling the advanced situations needed to process the downloaded web pages. The following settings are changed
here:
- Automatically check for Internet Explorer updates - Determines if the browser checks the Internet
for the availability of newer versions of itself. When enabled, the browser will check approximately every
30 days and notify the user if a newer version is available. This setting has different effects based
on the version of the Windows operating system, but is suggested to keep this setting as enabled.
- Enable Install On Demand(Internet Explorer) - Determines if the browser will automatically download
and install Internet Explorer web components needed to display a webpage properly or perform tasks required by
a webpage. For example, when a webpage needs to display foreign language characters, Internet Explorer will
prompt to user to download the language pack and install this support pack when after it is downloaded if this
option is enabled. This ultimate goal of malicious code is to be downloaded and run on your computer. For
this reason, this setting should be disabled so malicious websites do not install and run their malicious
executable code.
- Enable Install On Demand (Other) - Determines if the browser will automatically download and install
third party web components needed to display a webpage properly. For the same reason as the previous setting,
this setting should be disabled.
- Enable offline items to be synchronized on a schedule - Determines if web pages that are downloaded
in order to be viewed when the computer is not online should be synchronized with website during times when
the computer is actually online. In order to view web pages offline, the web pages must be downloaded onto
your computer. It is a general rule of thumb not to allow your browser to automatically download data to your
computer, because there is always the chance that malicious code will find a way to exploit this automatic
action and download itself to your computer.
- Notify when downloads complete - Determines if the browser displays a message when an a user initiated
download is complete. This is a good way to confirm that the browser has completed what the user has
initiated.
- Use inline AutoComplete - Determines if the browser auto-completes entries in the Address Bar while
the user is typing in a URL. This auto-complete is based on the browser recalling the History of the website
addresses that the browser has visited. It is suggested not to store a browser history.
It is suggested to always use the most recently available updates software updates for the browser, to not allow the
browser to perform any actions automatically, to not store website data on your computer, to be aware of the status
of anything that is downloaded, and to not store information about the user in the browser. It is for these
suggestions respectively that these Browser options are set.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- These settings will restrict the browser's handling of downloads and storage of URL information that is entered into the
browser's address bar. These options typically add a certain level of convenience to the browser for the user, however
the side effect is that, if the browser is accessed by an attacker, all this information that is stored for convenience
to the user is then available to the attacker. Therefore, the consequences to the user are convenience of browser usage.
- Return
Internet Explorer: Security Options
- Why do this?
- The Security options that are adjusted pertain to configuring the browser for secure communication with web servers.
- Check for publisher's certificate revocation - Determines if the browser checks a software publisher to
verify that its certificate has not been revoked before accepted the software. A certificate is Internet Explorer's
method of identify software, so by checking the status of a certificate through a known verification site, the
user may be certain that the software is valid. It is suggested to enable this setting.
- Check for server certificate revocation - Determines if the browser checks a website's certificate to
verify that it has not been revoked before accepted the website's certificate as valid. A certificate is
Internet Explorer's method of software, so by checking the status of a certificate through a known
verification site, the user may be certain that the site is not being spoofed or invalid. It is suggested to
enable this setting.
- Check for signatures on downloaded programs - Determines if the browser checks the identity when a
program is downloaded. The identity takes the form of a signature used to verify that the downloaded file
is what is suppose to be. When this option is enabled, the browser will display the confirmed information
to the user when a download is initiated by the user. It is suggested to enable this option, because is easy
for malware disguise itself as a legitimate file.
- Do not save encrypted pages to disk - Determines if the browse stores the data needed to display secure
websites in the Temporary Internet Files folder. If a browser is allowed to save secure information to the
computer's temporary folder, this information will then be accessible to anyone who as access to this folder,
including malware or any users of the computer, until the temporary files are erased. This information could
include password information, credit card information, or an information that is saved on the computer during
secure website communication (HTTPS). It is suggested to enable this option to avoid saving of this secure
data.
- Empty Temporary Internet Files folder when browser is closed - Determines if the browser's temporary
storage of files need to display web pages is deleted when the browser is closed. It is suggested to enable
this option to remove any temporary storage if the browser is set to save temporary internet files. Temporary
files is a common place for malware to store files that it needs to perform an exploit, since the user sees these
files as temporary and typically disregards them.
- Enable Profile Assistant - Determines if the browser accepts requests for Personal Assistant from
websites that send request user personal information. The browser will be default prompt the user prior to
sharing any personal information with a website, however it is suggested to disable this setting to prevent
accidental sharing of any personal information that may be saved by the browser.
- User SSL 2.0 - Determines if the browser transmits and receives secure data through the Secure Sockets Layer
Level 2 communications protocol. All secure websites support this communication standard, however there are exploits
that also are able to take advantage of the Microsoft Secure Socket Layer library and compromise computers using
SSL 2.0 encryption. These exploits are able to give malicious attackers access to the browser's computer and
administrative rights on the affected computer. It is suggested to disable this option so that the browser does not
use this insecure transmission.
- User SSL 3.0 - Determines if the browser transmits and receives secure data through the Secure Sockets Layer
Level 3 communications protocol. SSL 3.0 is intended to succeed SSL 2.0 and is therefore more secure. It is
suggested to enable this option in order to force the browser to use this form of encrypted communication over SSL 2.0.
- User TLS 1.0 - Determines if the browser transmits and receives secure data through the Transport Layer Security
communications protocol, which is an open security communication standard. It is suggested to use this form of secure
communications when available.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- These options may inhibit the browsing because they determine if communications are allowed between the browser and a
website. It is very easy to intercept and modify communications between a browser and web server so it is suggested to
force usage of secure communications and check that a websites has been certified prior to communicating with it. The
result of this is to ensure that data is not stored to the hard drive where it is available to spyware. This will
protect the user from some phishing scams and will make sure they only receive data from verified sources.
As far as drawbacks are concerned, the user should not experience any change in their browsing experience, unless they
are accessing secure websites that don’t support the enabled secure communications protocol.
- Return
Firefox: Privacy Options
- These settings dictate how Firefox handles information concerning the user's browsing experience, in particular information
about the user and the websites that the user visits. Typically, these settings provide features to make surfing more convenient
for the user, and not imperative for using the browser. A general rule of thumb is that is not a good idea to let the browser
gather information about its user. Although it provides a convenience to the user, this personal information must be stored
locally on the browser's computer and is just as easily accessed by the browser as well as malware. The suggestions made
for these settings will allow the user to secure their identity while online.
Firefox: Privacy Option: History
- Why do this?
- This browser will remember links to the websites that it has recently visited. By setting the value to zero, the
browser history is in effect disabled. The result of disabling the browsers history is that malware and spyware
are not able to harvest surfing trend information and other personal information about the user from the browser's
history log.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- This may have a slightly annoying effect because the user is not able to look up URL addresses that they have
recently visited. However, the user may also achieve the history effect by creating Bookmarks for each desired
URL address.
- Return
Firefox: Privacy Option: Saved Form Information
- Why do this?
-
- The browser will remember information that is entered into webpage forms and the browser Search Bar. The intention
here is facilitating the user's web browsing experience by automatically making suggestions when you enter information
again. It is best to not allow the browser to save any information that is entered into a web form. Although it
is convenient for the user to have the browser complete webpage forms, it is just as easy for malware to access this
saved information.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- This may have be annoying for some users since they will have to enter their personal information into all web forms,
but it will not impact the users browsing experience.
- Return
Firefox: Privacy Option: Saved Passwords
- Why do this?
-
- The browser will remember user passwords that are entered into webpage login forms in its Password Manager. The
intention here is convenience for the user not to recall their username and password when visiting sites that require
them to login in order to access the webpage. For example, the user may allow the browser to save their password for
their online banking account, and when they access this banking web site from the browser with their password saved,
the browser will automatically enter their password. It is best to disable the browser's ability to recall user
passwords. Although it is convenient for the user not to enter their login information every time they access the
website, it is just as easy for malware to access this saved information.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- This may be a slightly annoying on the user because they must enter their password on each website that requires a
password, but it will significantly reduce the ability of malware to capture their password information. Firefox
does allow the user to password protect the password information that it stores. In theory this will help protect
the user's password information, however it best to disassociate your password information from the browser. There
are password managers that are not associated with browsers and more secure at managing password information.
- Return
Firefox: Privacy Option: Download Manager History
- Why do this?
-
- The browser stores shortcuts to all the recent downloads that are initiated by the user, such as office productivity
software Microsoft Word, an Adobe PDF file, or hardware driver software. It is best to keep this list of downloaded
files clear so that what is being downloaded may be used by malware or prying eyes.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- Keeping this list of downloads clear will have no effect on the usage of the browser. It is general good practice
to use the Download Manager to verify when a download is complete, and then clear the list afterwards.
- Return
Firefox: Privacy Option: Cookies
- Why do this?
-
- A cookie is identifying information that is sent by a webpage to your browser and stored locally as a file on your
computer when a webpage is accessed by that browser. A copy of this cookie is then sent back by the browser
to the server every time browser access that server. Since it is theoretical impossible for a website to keep track
of all of its users, the intention behind cookies are to store its user information on the user's computer.
This information is typically unique to that the user's browsing experience. For example, a cookie may contain
information for an online shopping cart to keep track of and tell the website what the person has chosen to
purchase. Since this sensitive information is used to identify a user, disabling cookies will not allow the
browser to accept cookies and potentially store personal information that might be accessed by malware.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- Since a large portion of web pages use cookies in order to store information about the user's interaction with the web site,
disabling cookies will significantly impact the user's browsing experience. If it is necessary to view a webpage that
requires cookies,
- Check the checkbox in front of Allow sites to set cookies.
- Check the checkbox in front of for the originating Web site only.
- In the drop down box after Keep Cookies:, select until I close Firefox.
- Uncheck the checkbox in front of Allow sites to set cookies.
- Under the cookies option, click on the Exceptions button.
- In Address of the web site: in the Exceptions window, enter the URL of the webpage that you would like to set cookies on your computer.
- Click on the Allow button.
- Click the OK.
This will allow the entered web site to set cookies, so sensitive information may be available for a malware attack and
caution should be taken to protect this information stored in the cookies.
- Return
Firefox: Privacy Option: Cache
- Why do this?
-
- When a webpage is accessed, the browser will save the webpage locally on the computer. The next time this webpage is
accessed, the browser will check if it has been previously saved, and if it has been saved, it will load the webpage from
the locally saved copy. The intention here is to expedite the user's browsing experience, because the computer does not
have to download the webpage again. This information includes all necessary components (HTML, images, scripts...)
necessary to display the web page and is stored locally in a temporary directory on the computer. This information may
be accessed like any file on the computer by searching the computers file system directories. By setting this value to
zero, the cache is disabled. It is suggested that the cache be disabled to avoid malware and spyware from accessing the
history of the visited web pages.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- The user's browsing experience will be slightly slower because the browser must download a webpage every time that the user
wants to see the webpage. This will not be as apparent with faster Internet connection because the browser is able to quickly
download the newest version of the webpage, and the need to store temporary files on the computer is not necessary. However,
this will be very obvious in a computing environment where the Internet connection is slower, such as with dial-up connectivity.
In this situation, the user may elect to allot a certain amount of disk space for caching of web pages; the default disk space
that Firefox allots is 50MB. In this situation, it is suggested that the user Clear the cache when closing the browser to
avoid having these temporary internet files on the computer.
- Return
Firefox: Web Features Options
-
Firefox: Web Features Option: Block Popup Windows
- Why do this?
-
- Pop-ups are windows that are automatically opened by the browser forcing the user to view the displayed information.
Although some websites use pop-ups legitimately to show information that is pertaining to but not part of the website's
information, generally they are used as online advertising and considered annoying. The default setting for Firefox
is for it to block pop-ups, and this is the suggested setting to reduce the annoying nature of a popup.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- Some sites do make legitimate usage of pop-ups. For example, a text website might provide a link that, when clicked,
would open a popup window to display an image that is referred to in the website text. If pop-ups are blocked, then
Firefox would not allow the web site to open the popup and the link would appear to be functionless. You may enter
a website as a trusted website, allowing it to open pop-ups, by performing the following steps:
- Click on the Allowed Site button to the right of Block Popup Windows.
- In the Allowed Sites window that opens, enter the exact URL of the website you want to allow pop-ups into the box under Address of web site:.
- Click the Allow button.
- Repeat this steps to add additional websites.
- Click the OK button.
You will note that the website that you entered is listed on the Allowed Sites window with an Allow status.
The website that you entered will be now be allowed to use pop-ups. If there are other websites listed in the Allowed
Sites window, you can remove them as follows:
- Highlight the website by click on its URL in the list of sites on the Allowed Sites window.
- Click on the Remove Site button.
- Repeat this steps to remove additional websites.
- Click on the OK button.
- Return
Firefox: Web Features Option: Allow web sites to install software
- Why do this?
-
- Firefox allows the user to add functionality and customize their browser by installing modules of software in the
form of extensions, add-ons, and themes. It is generally not a good idea to allow websites to install software
on your computer; it is far too easy to be install malicious software disguised as something legitimate. This
functionality may be disabled by unchecking the checkbox in front this feature, and this is the suggested setting.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- Disabling this feature will also not allow the user to update their browser as Firefox issues software updates.
The user is able to create a list of trusted sites from which to allow software to be installed. To view this
list, perform the following steps:
- Click on the Allowed Site button to the right of Allow web sites to install software.
- In the Allowed Sites window that opens, enter the exact URL of the website you want to allow pop-ups into the box under Address of web site:.
- Click the Allow button.
- Repeat this steps to add additional websites.
- Click the OK button.
One suggested website to add as trusted is "update.mozilla.org". You will note that the website that you
entered is listed on the Allowed Sites window with an Allow status. The website that you
entered will be now be able to install software. If there are other websites listed in the Allowed
Sites window, you can remove them as follows:
- Highlight the website by click on its URL in the list of sites on the Allowed Sites window.
- Click on the Remove Site button.
- Repeat this steps to remove additional websites.
- Click on the OK button.
The user should be very skeptical of the sites that they allow to install software. It is common practice for malware to
emulate trusted sites.
- Return
Firefox: Web Features Option: Load Images
- Why do this?
-
- The default setting for Firefox is to load the images on a web page in order to allow for a pleasant surfing
experience. Some websites, however, load images from a server other the one hosting the website, such as with
a third party advertising site. A potential side effect of allowing these third party images is web bugs or
other hidden graphics. A web bug is a obtrusive graphic used for monitoring web traffic, profiling a
persons surfing habits, profiling what type of browser being used, counting the number of hits for a web pages
and is typically loaded from a web server other than the one hosting the web page. In order to avoid these web bugs,
it is suggested to enable loading images for the originating web site only.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- There are no consequences for enabling this feature, unless the websites that you visit server web pages from more than
one web server. If the user encounters a server while surfing that they would like to block image loading, they may
manually block that server as follows:
- Right click on the image on the web page being viewed.
- In the context menu that appears, click Block Image from < server name >.
- Click on Tools on the Firefox menu bar.
- Click on Options....
- Click on the Web Features icon.
- Click on the Exceptions button to the right of Load Images.
- In the Exceptions window, the site the you blocked will be listed.
- Return
Firefox: Web Features Option: Enable Java
- Why do this?
-
- Java is a popular platform-independent programming language that is able to create web applications, however it is
a common target for malware authors. Malware takes advantage of the fact that it is executable code, which is
typically automatically downloaded and executed on your computer. Numerous exploits exist that use Java to
compromise a computer and the data stored on it. Disable Java within Firefox by unchecking this feature, this is
the suggested setting for this option due to Java's popularity as a language for creating malware.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- Java is self standing application called an applet that is used to create interactive web content (games,
animations, printing features...) and web based applications (mortgage calculators, image manipulations, virus
scanners...). If java is not disabled, Firefox will not allow any of the functionality achieved through the
Java applets. This will impact your browsing experience because the content provided by web sites for
legitimate purposes will be blocked. The benefit though is that the potential threat from Java based malware
is eliminated.
- Return
Firefox: Web Features Option: Enable JavaScript
- Why do this?
-
- JavaScript is a scripting language used to add functionality to web pages and thus integrated directly into the
webpage's HTML code. The intention here is alleviate the work load on the server and allow your computer to do some
of the work, additionally, the user's webpage interactions is much more responsive because the webpage does not
need to return to the web server in order to process information. JavaScript is used to create allot of custom web
page building blocks, such as form elements (drop down interactive menus, submit buttons...). Although there is an
added convenience for using JavaScript, it is still code that is technically executed on your machine without your
consent. It is for this reason the suggested setting is to disable JavaScript within Firefox.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- Many web sites depend on JavaScript, so disabling it will impact presentation of the web pages on your
computer. There is an Advanced button in the Web Features options that will allow the user to allow or
disallow certain tasks that JavaScript typically performs. If you see fit to use JavaScript in order to gain
this functionality but control its abilities, adjust these settings.
- Return
make a note somewhere that these settings should be checked on a regular basis to promote consistency of settings.
Firefox: Downloads Options
- These options determine how Firefox handles downloaded files. The setting made for these options will determine how secure
the user's system is in respect to what is downloaded from the Internet to the user's computer.
Firefox: Downloads Option: Download Folder
- Why do this?
-
- This allows the user to select one folder in which to save all the downloads from the Internet.
It is suggested to save all downloads that you initiate to a centrally located folder. This facilitates scanning
of downloaded files, since they are centrally located. Keep in mind that these downloads are not the temporary
files that Firefox keeps when downloading web pages.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- There are no consequences to saving to other locations, however, the user is better able to manage their system
by saving all downloads to one file folder.
- Return
Firefox: Downloads Option: Download Manager
- Why do this?
-
- This allows the user to see the download process take place, allowing the user to cancel the download if the need
arises, and they can also verify that the download has occurred. Additionally, it also recalls all the files
downloaded by Firefox so the user is able to keep record of what has been downloaded and easily accessed the
downloaded file by viewing the Download Manger. To view the Download Manager:
- On the Firefox menu bar, click on Tools.
- Click on Downloads.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- There is not consequences to not using disabling the Download Manager, however, the user is better able to manage
their system because they have a reference for all the downloads.
- Return
Firefox: Downloads Option: File Types
- Why do this?
-
- This option allows Firefox to automatically perform a specified action for a downloaded file based on the file's
file type. When a file is downloaded, if the user has associated an executable with the file extension of the
downloaded file, Firefox will launch the executable to load the downloaded file. If there is no association with
the downloaded file's extension, Firefox will save the file to the specified download Folder. This is something
that is built into Microsoft Internet Explorer; however, it is suggested not to automatically perform actions on
download files so all files should be removed from this list. Firefox will reference this list every time
a file is downloaded; if the file type is not on this list it will add it to the list and prompt the user for an
association for this new file type. It is suggested that the user select Save to Disk.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- There are no consequences with adjusted this setting, in fact it will allow the user to better manager their
system because they will have to manually associate the downloaded file with the executable to run it.
- Return
Firefox: Advanced Options
- The advanced options contain settings specific to an advanced user, allowing them to tweak the browser to its highest security
level.
Firefox: Advanced Option: Software Update
- Why do this?
-
- Firefox is able to check for updates for itself, installed extensions, and installed themes, and notify the user
when new updates are available for downloading. Mozilla continuously provides updates that address both
functionality and security updates to it users. It is suggested to allow Firefox to automatically check if are
available, and install them when they are available. It is good practice to always use the latest version of
Firefox software in order to ensure maximum stability and security of the browser.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- There are no consequences from enabling the Software Updates feature. There are however consequences from being
out of date with Firefox updates.
- Return
Firefox: Advanced Option: Security
- Why do this?
-
- This security setting specifies if the browser uses secure transmission of information through Secured Sockets
Layer(SSL) and Transport Layer Security(TLS) to communication with secure websites. Although it would make
the browser the most versatile by selecting each of the available options, it is suggested to use the newest
versions of each of these methods of secure transmissions and to always use secure transmission when available.
The reason for this is because there exists exploits that are able to compromise SSL 2.0 encryption, giving the
attacker elevated user rights on the infected computer
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- There should be no noticeable changing in the browsing experience as a result of selection these options, but the
Firefox will be using the most securely encrypted communication available with those sites that allow it.
- Return
Firefox: Advanced Option: Certificates
- Why do this?
-
- Certificates contain the information for encryption and decryption for communication between the browser and secure
sites. Simple stated, certificates allow the user to identify themselves. This setting dictates how the browser
will react when a websites prompts it for a certificate. It is suggested to adjust Firefox to always prompt the
user to manually select a certificate when a web site requests a secure session. This also allows the user to be
aware of the start of the secure session.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- This setting will have no visual changes in the operations of the browser.
- Return
Firefox: Advanced Option: Validation
- Why do this?
-
- When using certificates, it is best to make sure that those used by Firefox are not obsolete, this is referred to as
validation. The Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) is the method used to check the validation every time
that a certificate is used. It is suggested to enable Firefox to check the validity of certificates every time
they are used.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- This setting will have no visual changes in the operations of the browser, however the level of secure communication
will be heightened because the browser will check for a certificate's validity each time the certificate is
viewed or used.
- Return
Opera: General Preferences
- The General preferences pertain to the browsers basic operation. For the purposes of securing the browser, the handling of Pop-ups
will be addressed.
Opera: General Preferences: Pop-ups
- Why do this?
-
- Pop-ups are windows that are automatically opened by the browser forcing the user to view the displayed information.
Although some websites use pop-ups legitimately to show information that is pertaining to but not part of the website's
information, generally they are used as online advertising and considered annoying. For example, a legitimate pop-up may
be a login page for a website. The available settings for controlling pop-ups are: Open all pop-ups, Open pop-ups in
background, Block unwanted pop-ups, Block all pop-ups. Base on this setting, the Opera browser will try and distinguish
between user requested and unwanted automatically pop-ups. The suggested setting to reduce the annoying nature of a popup
is Block unwanted pop-ups .
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- Some sites do make legitimately usage of pop-ups. For example, a text website might provide a link that, when clicked,
would open a popup window to display an image that is referred to in the website text. If pop-ups are blocked, then
Firefox would not allow the web site to open the popup and the link would appear to be functionless.
- Return
Opera: Wand Preferences
- The Wand preferences handle the browser's password manager and storage of the user's personal information.
Opera: Wand Preferences: The Wand
- Why do this?
-
- The browser is able to remember user passwords in its Password Manager call the The Wand. The
intention here is convenience for the user in that the browser manages their username and password for web sites that
require the user to login in order to access the webpage. For example, with this option is enabled, when the user
enters a new username and password, the browser will prompt the user if they would like to save this information.
If the user selects elects to utilize the browsers Password Manager, the next time they visit that web site, they
may login by simply clicking on the Wand button, which is on the address bar to the left of the URL. This may be very
convenient for some users for example with online banking account; when they access this banking web site from
the browser with their password saved, the browser will provide their password information. It is best to disable
the browser's ability to recall user passwords. Although it is convenient for the user to allow the browser to enter
their login information, it is just as easy for malware to access this saved information.
To elaborate on how Opera prompts the user to save a password, when the user enters their username and password
into a login webpage, the browser will prompt the user if they want the Wand to save this information. The user is
given four options by the browser to handle their password: For this page, For entire server, Never on this page, and
Never on entire server. It is suggested to select Never on entire server from this provided list of
options. To verify that the browser will not save user password for this server:
- On the menu bar, click Tools pulldown menu.
- Note: The Toolbar menu is the bar at the top of the Opera window.
- Under Tools, click on the Preferences... menu option.
- This will provide the Preferences window, which has a tabbed interface for adjusted the
browser's settings.
- Click on the Wand tab.
- Click on the Passwords button.
- In the Server manager window, look for the domain URL of the login website and click on it.
- In the expanded list of websites below this domain URL will be the URL of the login page,
to the right of the URL should be the option Never on entire server .
To avoid confusion, it is suggested to remove all websites from the Opera Server Manager for Wand logins, but the
user may instead verify that all listed login URL state Never on entire server.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- This may be a slightly annoying for the user since they will be required to enter their password on each
website that requires a password, but it will significantly reduce the ability of malware to capture their
password information. Opera does allow the user to set a password to protect the information stored by The Wand.
In theory this will help protect the user's password information, however it best to disassociate your password
information from the browser. There are password managers that are not associated with browsers and more secure
at managing password information.
- Return
Opera: Wand Preferences: Personal Information
- Why do this?
-
- It is common to enter your personal information into web forms, such as when shopping at e-commerce sites. Opera
is able to store this personal information, allowing you to enter this information in the web forms by
either selecting it from drop down lists or by right clicking the input field and selecting Insert Personal
from the context menu. The intention here is facilitating the user's web browsing experience by automatically
entering commonly entered fields. It is best to disable this option and not allow the browser to save any
personal information about the user. Although it is convenient for the user to have the browser complete webpage
forms, it is just as easy for malware to access this saved information.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- This may have be annoying for some users since they will have to enter their personal information into all web forms,
but it will not impact the users browsing experience.
- Return
Opera: Advanced Preferences
- The Advanced preferences handle all the fine details about the user's browsing experience. These settings help to create another
barrier between your computer and potential attackers, and help to upgrade the security that Opera employs so it is harder for an
attacker to exploit your system. This settings includes how the browser handles the webpage content provided by a website,
any user initiated downloads, the browser's history, and the browser security.
Opera: Advanced Option: Java Option
- Why do this?
-
- JavaScript is a scripting language used to add functionality to web pages and thus integrated directly into the
webpage's HTML code. The intention here is alleviate the work load on the server and allow your computer to do some
of the work, additionally, the user's webpage interactions is much more responsive because the webpage does not need
to return to the web server in order to process information. JavaScript is used to create allot of custom web page
building blocks, such as form elements (drop down interactive menus, submit buttons...). Although there is an added
convenience for using JavaScript, it is still code that is technically executed on your machine without your
consent. It is for this reason the suggested setting is to disable JavaScript within Opera.
Java is a popular platform-independent programming language that is able to create web applications, however it is
a common target for malware authors. Malware takes advantage of the fact that it is executable code, which is
typically automatically downloaded and executed on your computer. Numerous exploits exist that use Java to
compromise a computer and the data stored on it. Disable Java within Opera by unchecking this feature, this is
the suggested setting for this option due to Java's popularity as a language for creating malware.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- Many web sites depend on Java and JavaScript, so disabling them will impact presentation of the web pages on your
computer. There is a JavaScript button in the Content options of the Advanced Preferences that will
allow the user to either allow or disallow certain tasks that JavaScript typically performs. If you see fit to use
JavaScript in order to gain this functionality but control its abilities, adjust these settings. The benefit though
that the potential threat from Java based malware is eliminated.
- Return
Opera: Advanced Option: Downloads Options
- Why do this?
-
- This allows the user to select one folder in which to save all the downloads from the Internet.
It is suggested to save all downloads that you initiate to a centrally located folder. This facilitates scanning
of downloaded files, since they are centrally located. Keep in mind that these downloads are not the temporary
files that Opera keeps when downloading web pages.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- There are no consequences to saving to other locations, however, the user is better able to manage their system
by saving all downloads to one file folder.
- Return
Opera: Advanced Option: Browser History and Cache Options
- Why do this?
-
- This browser will remember links to the websites that it has recently visited. By setting these values to zero,
the browser's history is in effect disabled. The result of disabling the browser's history is that malware and spyware
are not able to harvest surfing trend information and other personal information about the user from the browser's
history log.
When a webpage is accessed, the browser will save the webpage locally on the computer. The next time this webpage is
accessed, the browser will check if it has been previously saved, and if it has been saved, it will load the webpage from
the locally saved copy. The intention here is to expedite the user's browsing experience, because the computer does not
have to download the webpage again. This information includes all necessary components (HTML, images, scripts...)
necessary to display the web page and is stored locally in a temporary directory on the computer. This information may
be accessed like any file on the computer by searching the computers file system directories. By setting these values to
Off, the cache is disabled. It is suggested that the cache be disabled to avoid malware and spyware from accessing the
history of the visited web pages.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- This may have a slightly annoying effect because the user is not able to look up URL addresses that they have
recently visited. However, the user may also achieve the history effect by creating Bookmarks for each desired
URL address.
The user's browsing experience will be slightly slower because the browser is then forced to download a webpage every time
that the user wants to see this particular webpage. With faster Internet connections this is not as large a concern
because the browser is able to quickly download the webpage resulting in no need for temporary browser files on the
computer. However, this will be very obvious in a computer environment where the Internet connection is slower,
such as with dial-up connectivity.
- Return
Opera: Advanced Option: Cookie Options
- Why do this?
-
- A cookie is identifying information that is sent by a webpage to your browser and stored locally as a file on your
computer when a webpage is accessed by that browser. A copy of this cookies is then sent back by the browser
to the server every time browser access that server. Since it is theoretical impossible for a website to keep track
of all of its users, the intention behind cookies are to store its user information on the user's computer.
This information is typically unique to that the user's browsing experience. For example, a cookie may contain
information for an online shopping cart to keep track of and tell the website what the person has chosen to
purchase. Since this sensitive information is used to identify a user, disabling cookies will not allow the
browser to accept cookies and potentially store personal information that might be accessed by malware.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- Since a large portion of web pages use cookies in order to store information about the user's interaction with the web site,
disabling cookies will significantly impact the user's browsing experience. For example, many e-commerce sites and
bulletin boards will be rendered unusable because they track user progress through cookie data.
- Return
Opera: Advanced Option: Security Options
- Why do this?
-
- There exist exploits that are able to exploit the Microsoft Secure Socket Layer library and compromise machines using SSL 2.0
encryption. These exploits can give malicious attackers access to your computer including administrative rights, which allow the
attacker to execute code without the user knowing. Disabling
SSL 2.0 encryption will keep your machine safe from this exploit.
- What consequences will there be on my system?
- These options will result in more pop-up warnings from Opera, and inaccessibility of older, very insecure sites.
As for SSL2, your browsing experience will remain mostly unchanged. Most browsers and servers have the ability to use different
encryption methods should others fail.
- Return
 accesses since January 4, 2007
accesses since January 4, 2007
 copyright notice
copyright notice
 accesses since January 4, 2007
accesses since January 4, 2007


